As of now, there are quite a few welding processes and types of welding. Understanding the differences between these welding processes is crucial if you want to choose the correct one for you.
This welder types comparison guide will reveal the different welding types and there uses.
Some of them are very rudimentary, but some of them are very advanced. These welding techniques differ from relatively simple, to extremely complicated, so it's important you decide which type is right for you.
However, for somebody working in a chop shop or looking to so some welding at home, there are four standard welding processes you need to know about: TIG, MIG, Stick and Arc Welding.
(Check out our review on the best multi process welder that combines them all!)
Whether you are an expert looking for the best metal miter saws and tools to cut metal or If you’re a beginner and looking to learn the basics, you’ve come to the right place.
The best type of welding depends on exactly what you want to achieve and in this guide we'll go through the four standard types.
Our little guide will take you through all the welding processes including the four major of the welding types. We'll even go over mig vs tig welding.
So, without further ado, let’s get going!
What Are The 4 Types Of Welding?
These are the main 4 types of welding techniques. Keep reading below for more info regarding the welding processes and detailed information about each welding type.
MIG Welding
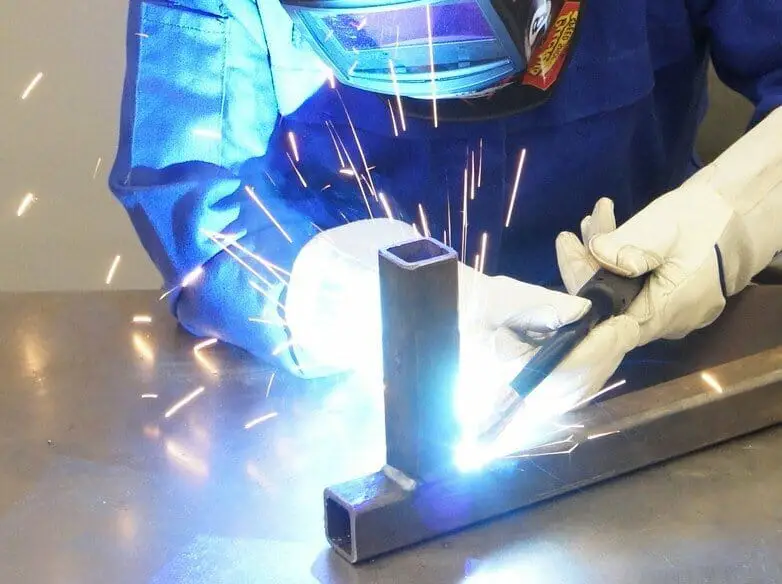

HOW DOES IT WORK?
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), most commonly known as MIG welding , is the process of continuously feeding a line of electrodes through a specialized “gun”.
In the gas metal arc welding process the electrode forms an arc with the base metal you’re trying to weld and then melts, fusing the material together.
The entire MIG welding processes uses a protective gas bubble that protects the weld from the ambient air and the components within it.
It should also be said that, because a wire is being fed to the material, the pieces being welded together aren’t actually being fused, which provides you with the opportunity to weld different kinds of metals together.
Naturally, because the MIG welder uses a “consumable” you will have to replace the electrode after some time. Also, the gas that forms the protective bubble needs to be replaced occasionally too.
What Can MIG Welding Be Used For?
So, what do you use the gas metal arc welding type of welding for?
It should be said that the MIG welding processes can be applied in various situations.
A good MIG welder should be able to weld both thick and thin sheets of metal.
Quality machines have a wide power output range and a gauge that will let you adjust the power, allowing you to approach softer material without fear of burning through it.
At the same time they’re still powerful enough to weld thick steel pipes and provide a strong connection.
Is it the best type of welder? Let's first go through the advantage and disadvantages of each.
What Are The Main Advantages of MIG Welders?
Disadvantages of MIG Welding
TIG Welding
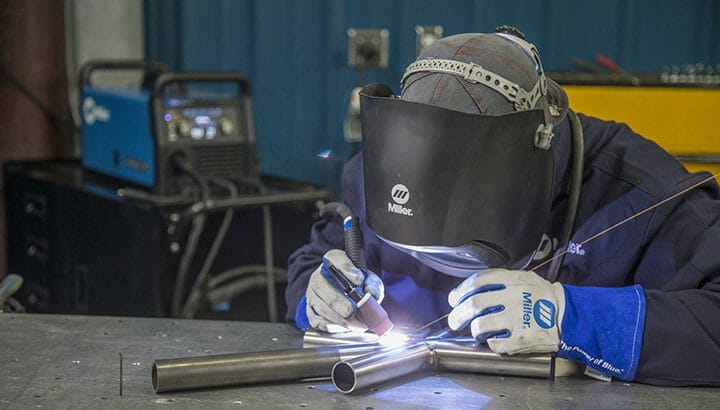

HOW DOES IT WORK?
In this welder types comparison guide TIG welding is one of the more popular types of welding processes. Many people are interested in the tig vs arc welding debate.
TIG, Heliarc or GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) is a welding process where a non-consumable tungsten electrode is used to heat up the material and melt it, creating a weld puddle.
Unlike GMAW, gas tungsten arc welding is produced from a single metal type, because there is no filler metal used for the weld. These Welding processes have highly evolved in recent years giving it more everday uses and making it easier for the avarage person.
However, you can add another rod to provide a filler material for you, so that the welding process can be applied to more materials or different metals at once.
Just like GMAW, these welding processes requires a gas bubble to protect the weld from contaminants. The gases used with TIG are usually helium or argon, whereas you would use carbon dioxide for MIG.
Because there is no feeding involved, there is no need to replace the electrode, only refill the gas tank. That is a big advantage for gas tungsten arc welding.
What Can TIG Welding Be Used For?
Similar to other types of welding processes, GTAW (or gas tungsten arc welding) can be applied to many materials.
However, the thickness range of this welding type is more limited.
Though you can weld both steel and aluminum with the same ease, the materials you will be welding are going to be thinner.
The tungsten rod is much thinner than a stick rod, allowing you to make more precise but much thinner welds.
What Are The Main Advantages?
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
Stick Welding

HOW DOES IT WORK?
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) or stick welding is one of the oldest types of the welding processes.
It is very simplistic in how it works but produces exceptionally strong welds, and it can be used to weld the thickest of materials.
The way stick welding works is through a single electrode that also provides most of the welding material. The electrode gets heated, then melts, but the intense heat melts the workpiece and welds the two parts together. The rod is also coated in flux, which creates a shield around the weld, protecting it from contamination.
Stick welding uses a consumable rod, and this rod will need to be changed frequently as you continue to weld.
What Can Stick Welding Be Used For?
Stick welding is a type of arc welding, and is widely used in construction because of the strength of this weld.
It's the way to go for thick materials, including cast iron - which can be tough or impossible for other welding types.
But when you want to have two pieces of thick metal fused together, and to make sure the weld is going to last, this is the way to go.
Advantages of Stick Welding
Disadvantages of Stick Welding
Arc Welding (Flux Core)
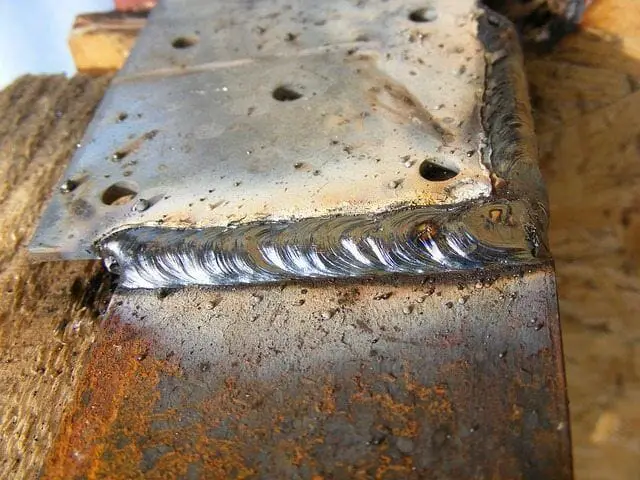

HOW DOES IT WORK?
At last, we come to our final welding type, arc, or flux-cored, welding.
This welding type is very similar to other types of welding, for example MIG welding. They both use a consumable wire that is being constantly fed to the weld. However, this is where the two begin to differ.
In arc welding, the wire used has a flux core that immediately generates a gas shield around the weld, whereas you need an external gas supplement for MIG.
There is also something known as dual-shielded welding, which uses another external gas supply to form a second shield for an even more secure weld.
Naturally, since there is a consumable, you will have to replace it once in a while.
However, unlike MIG, you don’t need to refill a gas tank if you don’t intend to use dual-shielded arc welding.
What Can Arc Welding Be Used for?
When using flux-cored welding style, you will want to use it with heavier and thicker materials.
Flux-cored welding also creates more heath then types of welding and you will want to use it where there is enough base metal to withstand that much heat.
This type is primarily used for heavy steel construction and erection, heavy repairs and heavy machinery and other such equipment.
What Are The Main Advantages?
Disadvantages of Arc Welding
mig vs tig welding
Both MIG and TIG welding use an electric arc to create the weld. However the one big difference between them both is the arc process.
MIG welding uses a feed wire that continuously moves through the gun to create a spark. This process melts and this is what forms the weld.
TIG welding, conversely, uses longer rods to combine two metals directly together.
Conclusion
To reiterate, our goal here is to reveal welder types comparison between the four standard types of welding. Although there are other welding types, (flux-cored arc welding, gas welding, Plasma Arc Welding & Laser Welding) these are the most popular four.
As we said, MIG is the most versatile and the easiest one to learn; TIG is the most aesthetically pleasing; stick and arc produce the strongest welds and can operate under less than desirable conditions.
We also discussed the best beginner’s welder and the type that produces the strongest weld.
After all of this, the choice is, of course, yours.
What is the best type of welding? Whether you want to start easy with an MIG welder, or you want to master game at the hardest difficulty with a TIG welder, you will go with the welder that interest you the most.
FAQs
1. What are the 5 types of welding?
What types of welding are there?
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding - Metal Arc Welding with a Gas Metal Arc (GMAW)
- TIG Welding - Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (GTAW)
- Stick Welding - Metal Arc Shielded Welding (SMAW)
- Flux-Corrosion Welding - Arc Welding with a Cored Arc (FCAW)
- Welding with an Energy Beam (EBW)
- Welding of Atomic Hydrogen (AHW)
- Tungsten-Arc Gas Welding
- Arc Plasma Welding.
2. Which welding is strongest?
TIG welding.
TIG welding produces stronger welds that are cleaner and more precise than MIG welding or other Arc welding methods. Having said that, different welding jobs may require different methods; while TIG welding is generally stronger and of higher quality, you should use MIG or another method if the job requires it.
3. Which gas is used in welding?
Shielding gases such as carbon dioxide, argon, and helium are used in welding and cutting processes. oxygen, which is used in conjunction with fuel gases and also in trace amounts in some shielding gas mixtures.
4. What is G in welding?
It entails welding on the joint's top side. The molten metal is drawn downward into the joint in this position. As a result, welding becomes faster and easier. The number 1 denotes the flat position in 1G and 1F, while the letter G denotes a groove weld and the letter F denotes a fillet weld.
5. What is the easiest type of welding?
Metal inert gas welding.
MIG welding (metal inert gas welding) is frequently regarded as the simplest type of welding to learn for a beginner. MIG welders use a spool of wire welding electrodes that are fed through a welding gun at a predetermined speed.